Once you have a volume, create at least one share so that the storage is accessible by the other computers in your network. The type of share you create
depends upon the operating system(s) running in your network, your security requirements, and expectations for network transfer speeds.
If you are looking for a solution that allows fast access from any operating system, consider configuring the FTP service instead of a share and use a
cross-platform FTP and file manager client application such as
Filezilla. Secure FTP can be configured if the data needs to be encrypted.
If data security is a concern and your network’s users are familiar with SSH command line utilities or
WinSCP, consider configuring the SSH service instead of a share. It will be slower than unencrypted FTP due to the overhead of
encryption, but the data passing through the network will be encrypted.
This section will demonstrate how to create AFP, NFS, CIFS, WebDAV, and iSCSI shares. FTP and SSH configurations are described in
Services Configuration.
10.1. Apple (AFP) Shares
FreeNAS® uses the
Netatalk
AFP server to share data with Apple systems. Configuring AFP shares is a multi-step process that requires you to create or import users and groups, set
volume/dataset permissions, create the AFP share(s), configure the AFP service, then enable the AFP service in .
This section describes the configuration screen for creating the AFP share. It then provides configuration examples for creating a guest share, configuring
Time Machine to backup to a dataset on the FreeNAS® system, and for connecting to the share from a Mac OS X client.
If you click , you will see the screen shown in Figure 10.1a.
Figure 10.1a: Creating an AFP Share
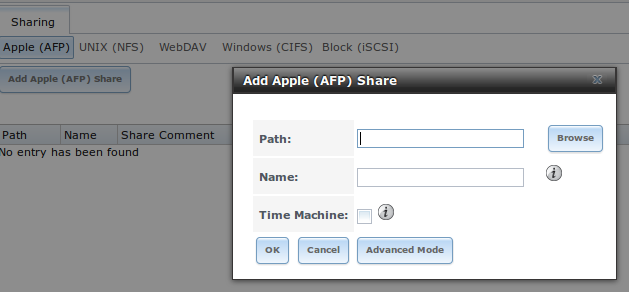
Table 10.1a summarizes the available options when creating an AFP share. Some settings are only available in “Advanced Mode”. To see these settings, either
click the “Advanced Mode” button or configure the system to always display these settings by checking the box “Show advanced fields by default” in
. Refer to
Setting up Netatalk
for a more detailed explanation of the available options.
Once you press the “OK” button when creating the AFP share, a pop-up menu will ask “Would you like to enable this service?” Click “Yes” and
will open and indicate whether or not the AFP service successfully started.
Table 10.1a: AFP Share Configuration Options
| Setting |
Value |
Description |
|---|
| Path |
browse button |
browse to the volume/dataset to share; do not nest additional volumes, datasets, or symbolic links beneath
this path because Netatalk lacks complete support |
| Name |
string |
volume name that will appear in the Mac computer’s “connect to server” dialogue; limited to 27 characters
and can not contain a period |
| Share Comment |
string |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; optional |
| Allow List |
string |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; comma delimited list of allowed users and/or groups where groupname
begins with a @; note that adding an entry will deny any user/group that is not specified |
| Deny List |
string |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; comma delimited list of denied users and/or groups where groupname
begins with a @; note that adding an entry will allow all users/groups that are not specified |
| Read-only Access |
string |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; comma delimited list of users and/or groups who only have read access
where groupname begins with a @ |
| Read-write Access |
string |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; comma delimited list of users and/or groups who have read and write
access where groupname begins with a @ |
| Time Machine |
checkbox |
when checked, FreeNAS will advertise itself as a Time Machine disk so it can be found by Macs; due to a
limitation in how Mac deals with low-diskspace issues when multiple Mac’s share the same volume, checking
“Time Machine” on multiple shares may result in intermittent failed backups |
| Zero Device Numbers |
checkbox |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; enable when the device number is not constant across a reboot |
| No Stat |
checkbox |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; if checked, AFP won’t stat the volume path when enumerating the volumes
list; useful for automounting or volumes created by a preexec script |
| AFP3 UNIX Privs |
checkbox |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; enables Unix privileges supported by OSX 10.5 and higher; do not enable
if the network contains Mac OS X 10.4 clients or lower as they do not support these |
| Default file permission |
checkboxes |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; only works with Unix ACLs; new files created on the share are set with
the selected permissions |
| Default directory permission |
checkboxes |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; only works with Unix ACLs; new directories created on the share are set
with the selected permissions |
| Default umask |
integer |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; umask for newly created files, default is 000 (anyone can read, write,
and execute) |
| Hosts Allow |
string |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; comma, space, or tab delimited list of allowed hostnames or IP addresses |
| Hosts Deny |
string |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; comma, space, or tab delimited list of denied hostnames or IP addresses |
10.1.1. Connecting as Guest
AFP supports guest logins, meaning that all of your Mac OS X users can access the AFP share without requiring their user accounts to first be created on or
imported into the the FreeNAS® system.
Note
if you create a guest share as well a share that requires authentication, AFP will only map users who login as guest to the guest share. This means
that if a user logs in to the share that requires authentication, the permissions on the guest share may prevent that user from writing to the guest share.
The only way to allow both guest and authenticated users to write to a guest share is to set the permissions on the guest share to 777 or to add the
authenticated users to a guest group and set the permissions to 77x.
In this configuration example, the AFP share has been configured for guest access as follows:
- A ZFS volume named /mnt/data has its permissions set to the built-in nobody user account and
nobody group.
- An AFP share has been created with the following attributes:
- “Name”: freenas (this is the name that will appear to Mac OS X clients)
- “Path”: /mnt/data
- “Allow List”: set to nobody
- “Read-write Access”: set to nobody
- has been configured as follows:
- “Guest Access”: checkbox is checked
- nobody is selected in the “Guest account” drop-down menu
Once the AFP service has been started in , Mac OS X users can connect to the AFP share by clicking
. In the example shown in Figure 10.1b, the user has input afp:// followed by the IP address of the FreeNAS®
system.
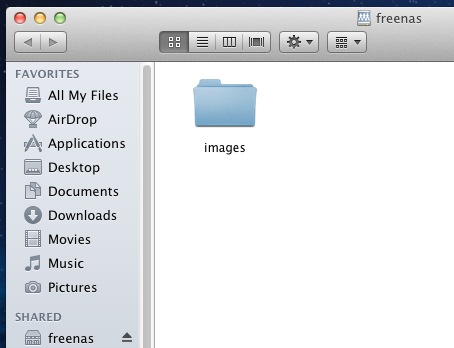
Click the “Connect” button. Once connected, Finder will automatically open. The name of the AFP share will be displayed in the SHARED section in the left
frame and the contents of the share will be displayed in the right frame. In the example shown in Figure 10.1c, /mnt/data has one folder named images.
The user can now copy files to and from the share.
Figure 10.1b: Connect to Server Dialogue
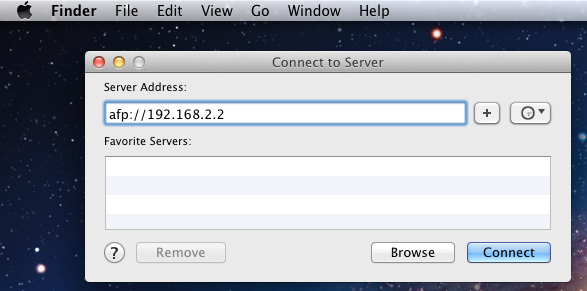
Figure 10.1c: Viewing the Contents of the Share From a Mac System
To disconnect from the volume, click the “eject” button in the “Shared” sidebar.
10.1.2. Using Time Machine
Mac OS X includes the Time Machine application which can be used to schedule automatic backups. In this configuration example, Time Machine will be configured
to backup to an AFP share on a FreeNAS® system. To configure the AFP share on the FreeNAS® system:
- A ZFS dataset named /mnt/data/backup_user1 with a “Quota” of 60G and a “Share type” of
Mac was created in .
- A user account was created as follows:
- “Username”: user1
- “Home Directory”: /mnt/data/backup_user1
- the “Full Name”, “E-mail”, and “Password” fields were set where the “Username” and “Password” match the values for the user on the Mac OS X system
- An AFP share with a “Name” of backup_user1 has been created with the following attributes:
- “Path”: /mnt/data/backup_user1
- “Allow List”: set to user1
- “Read-write Access”: set to user1
- “Time Machine”: checkbox is checked
- has been configured as follows:
- “Guest Access”: checkbox is unchecked
- The AFP service has been started in .
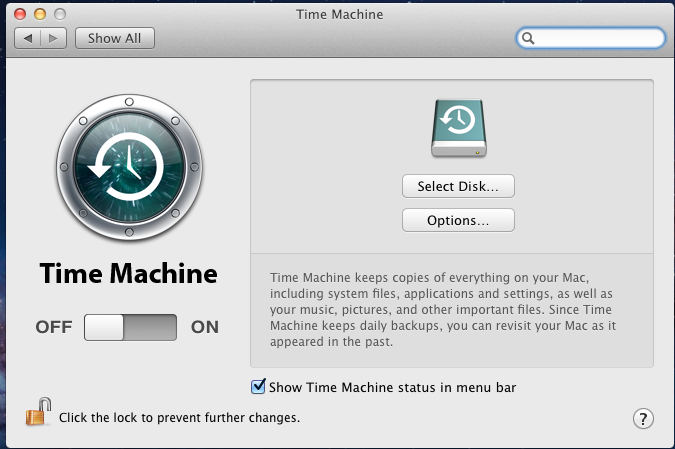
To configure Time Machine on the Mac OS X client, go to which will open the screen shown in Figure 10.1d.
Click “ON” and a pop-up menu should show the FreeNAS® system as a backup option. In our example, it is listed as backup_user1 on “freenas”. Highlight the
entry representing the FreeNAS® system and click the “Use Backup Disk” button. A connection bar will open and will prompt for the user account’s password–in
this example, the password for the user1 account.
Time Machine will create a full backup after waiting two minutes. It will then create a one hour incremental backup for the next 24 hours, and then one backup
each day, each week and each month.
Since the oldest backups are deleted when the ZFS dataset becomes full, make sure that the quota size you set is sufficient to hold the backups. Note that
a default installation of Mac OS X is ~21 GB in size.
If you receive a “Time Machine could not complete the backup. The backup disk image could not be created (error 45)” error when backing up to the FreeNAS®
system, you will need to create a sparsebundle image using
these instructions.
If you receive the message “Time Machine completed a verification of your backups. To improve reliability, Time Machine must create a new backup for you.” and
you do not want to perform another complete backup or lose past backups, follow the instructions in this
post. Note that this can occur after performing a
scrub as Time Machine may mistakenly believe that the sparsebundle backup is corrupt.
Figure 10.1d: Configuring Time Machine on Mac OS X Lion
10.2. Unix (NFS) Shares
FreeNAS® supports the Network File System (NFS) for sharing volumes over a network. Once the NFS share is configured, clients use the mount
command to mount the share. Once mounted, the share appears as just another directory on the client system. Some Linux distros require the installation of
additional software in order to mount an NFS share. On Windows systems, enable Services for NFS in the Ultimate or Enterprise editions or install an NFS
client application.
Note
for performance reasons, iSCSI is preferred to NFS shares when FreeNAS is installed on ESXi. If you are considering creating NFS shares on ESXi,
read through the performance analysis at
Running ZFS over NFS as a VMware Store.
Configuring NFS is a multi-step process that requires you to create NFS share(s), configure NFS in , then start NFS in
. It does not require you to create users or groups as NFS uses IP addresses to determine which systems are
allowed to access the NFS share.
This section demonstrates how to create an NFS share, provides a configuration example, demonstrates how to connect to the share from various operating
systems, and provides some troubleshooting tips.
To create an NFS share, click , shown in Figure 10.2a.
Figure 10.2a: Creating an NFS Share
Once you press the “OK” button when creating the NFS share, a pop-up menu will ask “Would you like to enable this service?” Click “Yes” and
will open and indicate whether or not the NFS service successfully started.
Table 10.2a summarizes the options in this screen. Some settings are only available in “Advanced Mode”. To see these settings, either click the “Advanced
Mode” button or configure the system to always display these settings by checking the box “Show advanced fields by default” in
.
Table 10.2a: NFS Share Options
| Setting |
Value |
Description |
|---|
| Path |
browse button |
browse to the volume/dataset/directory to share; click “Add extra path” to select multiple paths |
| Comment |
string |
used to set the share name; if left empty, share name will be the list of selected “Path”s |
| Authorized networks |
string |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; space delimited list of allowed network addresses in the form 1.2.3.0/24
where the number after the slash is a CIDR mask |
| Authorized IP
addresses or hosts |
string |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; space delimited list of allowed IP addresses or hostnames |
| All directories |
checkbox |
if checked, the client can mount any subdirectory within the “Path” |
| Read only |
checkbox |
prohibits writing to the share |
| Quiet |
checkbox |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; inhibits some syslog diagnostics which can be useful to avoid some annoying
error messages; see
exports(5)
for examples |
| Maproot User |
drop-down menu |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; if a user is selected, the root user is limited to that user’s permissions |
| Maproot Group |
drop-down menu |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; if a group is selected, the root user will also be limited to that group’s
permissions |
| Mapall User |
drop-down menu |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; the specified user’s permissions are used by all clients |
| Mapall Group |
drop-down menu |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; the specified group’s permission are used by all clients |
| Security |
selection |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; choices are sys () or the following Kerberos options:
krb5 (authentication only),
krb5i (authentication and integrity), or
krb5p (authentication and privacy); if multiple security mechanisms are added to the “Selected” column using the
arrows, use the “Up” or “Down” buttons to list in order of preference |
When creating the NFS share, keep the following points in mind:
- The “Maproot” and “Mapall” options are exclusive, meaning you can only use one or the other–the GUI will not let you use both. The “Mapall” options
supersede the “Maproot” options. If you only wish to restrict the root user’s permissions, set the “Maproot” option. If you wish to restrict the
permissions of all users, set the “Mapall” options.
- Each volume or dataset is considered to be its own filesystem and NFS is not able to cross filesystem boundaries.
- The network or host must be unique per share and per filesystem or directory.
- The “All directories” option can only be used once per share per filesystem.
To better understand these restrictions, consider the following scenario where there are:
- 2 networks named 10.0.0.0/8 and
20.0.0.0/8
- a ZFS volume named volume1 with 2 datasets named dataset1 and dataset2
- dataset1 has a directory named directory1
Because of restriction #3, you will receive an error if you try to create one NFS share as follows:
- “Authorized networks” set to 10.0.0.0/8 20.0.0.0/8
- “Path” set to /mnt/volume1/dataset1 and /mnt/volume1/dataset1/directory1
Instead, you should select a “Path” of /mnt/volume1/dataset1 and check the “All directories” box.
However, you could restrict that directory to one of the networks by creating two shares as follows.
First NFS share:
- “Authorized networks” set to 10.0.0.0/8
- “Path” set to /mnt/volume1/dataset1
Second NFS share:
- “Authorized networks” set to 20.0.0.0/8
- “Path” set to /mnt/volume1/dataset1/directory1
Note that this requires the creation of two shares as it can not be accomplished in one share.
10.2.1. Example Configuration
By default the “Mapall” options shown in Figure 10.2a show as N/A. This means that when a user connects to the NFS share, they connect with the permissions
associated with their user account. This is a security risk if a user is able to connect as root as they will have complete access to the share.
A better scenario is to do the following:
- Specify the built-in nobody account to be used for NFS access.
- In the “Change Permissions” screen of the volume/dataset that is being shared, change the owner and group to nobody and set the permissions according to
your specifications.
- Select nobody in the “Mapall User” and “Mapall Group” drop-down menus for the share in .
With this configuration, it does not matter which user account connects to the NFS share, as it will be mapped to the nobody user account and will only
have the permissions that you specified on the volume/dataset. For example, even if the root user is able to connect, it will not gain
root access to the share.
10.2.2. Connecting to the Share
In the following examples, an NFS share on a FreeNAS® system with the IP address of 192.168.2.2 has been configured as follows:
- A ZFS volume named /mnt/data has its permissions set to the nobody user account and the
nobody group.
- A NFS share has been created with the following attributes:
- “Path”: /mnt/data
- “Authorized Network”: 192.168.2.0/24
- “MapAll User” and “MapAll Group” are both set to nobody
- the “All Directories” checkbox has been checked
10.2.2.1. From BSD or Linux
To make this share accessible on a BSD or a Linux system, run the following command as the superuser (or with sudo) from the client system. Repeat
on each client that needs access to the NFS share:
mount -t nfs 192.168.2.2:/mnt/data /mnt
The mount command uses the following options:
- -t nfs: specifies the type of share.
- 192.168.2.2: replace with the IP address of the FreeNAS® system
- /mnt/data: replace with the name of the NFS share
- /mnt: a mount point on the client system. This must be an existing,
empty directory. The data in the NFS share will be made available to the client in this directory.
The mount command should return to the command prompt without any error messages, indicating that the share was successfully mounted.
Note
if this command fails on a Linux system, make sure that the nfs-utils package is
installed.
Once mounted, this configuration allows users on the client system to copy files to and from /mnt (the mount point) and all files will be owned by
nobody:nobody. Any changes to /mnt will be saved to the FreeNAS® system’s /mnt/data volume.
Should you wish to make any changes to the NFS share’s settings or wish to make the share inaccessible, first unmount the share on the client as the
superuser:
10.2.2.2. From Microsoft
Windows systems can connect to NFS shares using Services for NFS (refer to the documentation for your version of Windows for instructions on how to find,
activate, and use this service) or a third-party NFS client.
Instructions for connecting from an Enterprise version of Windows 7 can be found at
Mount Linux NFS Share on Windows 7.
Nekodrive
provides an open source graphical NFS client. To use this client, you will need to install the following on the Windows system:
- 7zip
to extract the Nekodrive download files
- NFSClient and NFSLibrary from the Nekodrive download page; once downloaded, extract these files using 7zip
- .NET Framework 4.0
Once everything is installed, run the NFSClient executable to start the GUI client. In the example shown in Figure 10.2b, the user has connected to the
example /mnt/data share of the FreeNAS® system at
192.168.2.2.
Note
Nekodrive does not support Explorer drive mapping via NFS. If you need this functionality,
try this utility
instead.
Figure 10.2b: Using the Nekodrive NFSClient from Windows 7 Home Edition
10.2.2.3. From Mac OS X
To mount the NFS volume from a Mac OS X client, click on . In the “Server Address” field, input nfs:// followed by
the IP address of the FreeNAS® system and the name of the volume/dataset being shared by NFS. The example shown in Figure 10.2c continues with our example of
192.168.2.2:/mnt/data.
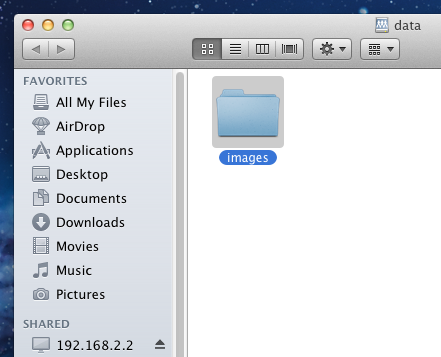
Once connected, Finder will automatically open. The IP address of the FreeNAS® system will be displayed in the SHARED section in the left frame and the
contents of the share will be displayed in the right frame. In the example shown in Figure 10.2d, /mnt/data has one folder named images. The
user can now copy files to and from the share.
Figure 10.2c: Mounting the NFS Share from Mac OS X
Figure 10.2d: Viewing the NFS Share in Finder
10.2.3. Troubleshooting NFS
Some NFS clients do not support the NLM (Network Lock Manager) protocol used by NFS. You will know that this is the case if the client receives an error that
all or part of the file may be locked when a file transfer is attempted. To resolve this error, add the option -o nolock when running the
mount command on the client in order to allow write access to the NFS share.
If you receive an error about a “time out giving up” when trying to mount the share from a Linux system, make sure that the portmapper service is running
on the Linux client and start it if it is not. If portmapper is running and you still receive timeouts, force it to use TCP by including -o tcp in your
mount command.
If you receive an error “RPC: Program not registered”, upgrade to the latest version of FreeNAS® and restart the NFS service after the upgrade in order
to clear the NFS cache.
If your clients are receiving “reverse DNS” errors, add an entry for the IP address of the FreeNAS® system in the “Host name database” field of
.
If the client receives timeout errors when trying to mount the share, add the IP address and hostname of the client to the “Host name data base” field of
.
10.3. WebDAV Shares
Beginning with FreeNAS® 9.3, WebDAV shares can be created so that authenticated users can browse the contents of the specified volume, dataset, or directory
from a web browser.
Configuring WebDAV shares is a two step process. First, create the WebDAV share(s) to specify which data can be accessed. Then, configure the WebDAV service
by specifying the port, authentication type, and authentication password. Once the configuration is complete, the share can be accessed using a URL in the
format:
protocol://IP_address:port_number/share_name
where:
- protocol: is either
http or
https, depending upon the “Protocol” configured in .
- IP address: is the IP address or hostname of the FreeNAS® system. Take care when configuring a public IP address to ensure that the network’s firewall
only allows access to authorized systems.
- port_number: is configured in . If the FreeNAS® system is to be accessed using a public IP address, consider
changing the default port number and ensure that the network’s firewall only allows access to authorized systems.
- share_name: is configured in .
Inputting the URL into a web browser will bring up an authentication pop-up message. Input a username of webdav and the password configured in
.
To create a WebDAV share, click which will open the screen shown in Figure 10.3a.
Figure 10.3a: Adding a WebDAV Share
Table 10.3a summarizes the available options.
Table 10.3a: WebDAV Share Options
| Setting |
Value |
Description |
|---|
| Share Path Name |
string |
input a name for the share |
| Comment |
string |
optional |
| Path |
browse button |
browse to the volume/dataset to share |
| Read Only |
checkbox |
if checked, users cannot write to the share |
| Change User & Group
Ownership |
checkbox |
if checked, automatically sets the share’s contents to the webdav user and group |
Once you click “OK”, a pop-up will ask if you would like to enable the service. Once the service starts, review the settings in
as they are used to determine which URL is used to access the WebDAV share and whether or not authentication is required
to access the share. These settings are described in WebDAV.
10.4. Windows (CIFS) Shares
FreeNAS® uses
Samba
to share volumes using Microsoft’s CIFS protocol. CIFS is built into the Windows and Mac OS X operating systems and most Linux and BSD systems pre-install
the Samba client which provides support for CIFS. If your distro did not, install the Samba client using your distro’s software repository.
Configuring CIFS shares is a multi-step process that requires you to set permissions, create CIFS share(s), configure the CIFS service in
, then enable the CIFS service in . If your Windows network has a Windows
server running Active Directory, you will also need to configure the Active Directory service in
. Depending upon your authentication requirements, you may need to create or import users and groups.
This section will demonstrate some common configuration scenarios. If you would like to use Shadow Copies, see Configuring Shadow Copies. If you are
having problems accessing your CIFS share, see Troubleshooting CIFS.
Figure 10.4a shows the configuration screen that appears when you click .
Figure 10.4a: Adding a CIFS Share
Table 10.4a summarizes the options when creating a CIFS share. Some settings are only available in “Advanced Mode”. To see these settings, either click the
“Advanced Mode” button or configure the system to always display these settings by checking the box “Show advanced fields by default” in
.
smb.conf(5)
provides more details for each configurable option. Once you press the “OK” button when creating the CIFS share, a pop-up menu will ask “Would you like to
enable this service?” Click “Yes” and will open and indicate whether or not the CIFS service successfully
started.
Table 10.4a: Options for a CIFS Share
| Setting |
Value |
Description |
|---|
| Path |
browse button |
select volume/dataset/directory to share |
| Use as home share |
checkbox |
check this box if the share is meant to hold user home directories; only one share can be the homes share |
| Name |
string |
mandatory; name of share |
| Comment |
string |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; optional description |
| Apply Default Permissions |
checkbox |
sets the ACLs to allow read/write for owner/group and read-only for others; should only be unchecked when
creating a share on a system that already has custom ACLs set |
| Export Read Only |
checkbox |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; prohibits write access to the share |
| Browsable to Network Clients |
checkbox |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; enables Windows clients to browse the shared directory using Windows
Explorer |
| Export Recycle Bin |
checkbox |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; deleted files are instead moved to a hidden .recycle directory
in the root folder of the share |
| Show Hidden Files |
checkbox |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; if enabled, will display filenames that begin with a dot (Unix hidden
files) |
| Allow Guest Access |
checkbox |
if checked, no password is required to connect to the share and all users share the permissions of the
guest user defined in the CIFS service |
| Only Allow Guest Access |
checkbox |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; requires “Allow guest access” to also be checked; forces guest access
for all connections |
| Hosts Allow |
string |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; comma, space, or tab delimited list of allowed hostnames or IP addresses;
see NOTE below |
| Hosts Deny |
string |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; comma, space, or tab delimited list of denied hostnames or IP addresses;
allowed hosts take precedence so can use ALL in this field and specify allowed hosts in
“Hosts Allow”; see NOTE below |
| VFS Objects |
selection |
only available in “Advanced Mode” and adds virtual file system modules to enhance functionality; Table
10.4b summarizes the available modules |
| Auxiliary Parameters |
string |
only available in “Advanced Mode”; additional smb4.conf parameters not covered by other option
fields |
Note
hostname lookups add some time to accessing the CIFS share. If you only use IP addresses, uncheck the “Hostnames lookups” box in
.
If you wish some files on a shared volume to be hidden and inaccessible to users, put a veto files= line in the “Auxiliary Parameters” field. The syntax for
this line and some examples can be found
here.
Table 10.4b: Available VFS Modules
| Value |
Description |
|---|
| audit |
logs share access, connects/disconnects, directory opens/creates/removes, and file opens/closes/renames/unlinks/chmods to syslog |
| extd_audit |
sends “audit” logs to both syslog and the Samba log files |
| fake_perms |
allows roaming profile files and directories to be set as read-only |
| netatalk |
eases the co-existence of CIFS and AFP shares |
| streams_depot |
experimental module to store alternate data streams in a central directory |
10.4.1. Share Configuration
The process for configuring a share is as follows:
If you are not using Active Directory or LDAP, create a user account for each user in with the following
attributes:
- “Username” and “Password”: matches the username and password on the client system
- “Home Directory”: browse to the volume to be shared
- Repeat this process to create a user account for every user that will need access to the CIFS share
If you are not using Active Directory or LDAP, create a group in . Once the group is created, click its
“Members” button and add the user accounts that you created in step 1.
Give the group permission to the volume in . When setting the permissions:
- set “Owner(user)” to nobody
- set the “Owner(group)” to the one you created in Step 2
- “Mode”: check the “write” checkbox for the “Group” as it is unchecked by default
Create a CIFS share in with the following attributes:
- “Name”: input the name of the share
- “Path”: browse to the volume to be shared
- keep the “Browsable to Network Clients” box checked
Note
be careful about unchecking the “Browsable to Network Clients” box. When this box is checked (the default), other users will see the names of
every share that exists using Windows Explorer, but they will receive a permissions denied error message if they try to access someone else’s share. If
this box is unchecked, even the owner of the share won’t see it or be able to create a drive mapping for the share in Windows Explorer. However, they
can still access the share from the command line. Unchecking this option provides limited security and is not a substitute for proper permissions and
password control.
Configure the CIFS service in as follows:
- “Workgroup”: if you are not using Active Directory or LDAP, set to the name being used on the Windows network; unless it has been changed, the default
Windows workgroup name is WORKGROUP
Start the CIFS service in . Click the click the red “OFF” button next to CIFS. After a second or so, it will
change to a blue “ON”, indicating that the service has been enabled.
Test the share.
To test the share from a Windows system, open Explorer and click on “Network”. For this configuration example, a system named FREENAS should appear with a
share named backups. An example is seen in Figure 10.4b:
Figure 10.4b: Accessing the CIFS Share from a Windows Computer
If you click on backups, a Windows Security pop-up screen should prompt for the user’s username and password. Once authenticated, the user can copy
data to and from the CIFS share.
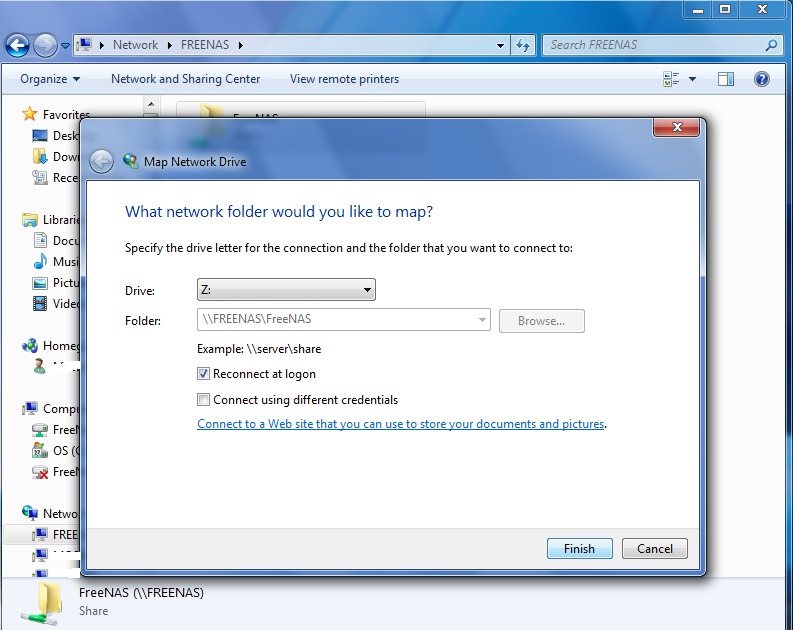
To prevent Windows Explorer from hanging when accessing the share, map the share as a network drive. To do this, right-click the share and select “Map network
drive...” as seen in Figure 10.4c:
Figure 10.4c: Mapping the Share as a Network Drive
Choose a drive letter from the drop-down menu and click the “Finish” button as shown in Figure 10.4d:
Figure 10.4d: Selecting the Network Drive Letter
10.4.2. Configuring Shadow Copies
Shadow Copies, also known as the Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) or Previous Versions, is a Microsoft service
for creating volume snapshots. Shadow copies allow you to easily restore previous versions of files from within Windows Explorer. Shadow Copy support is built
into Vista and Windows 7. Windows XP or 2000 users need to install the
Shadow Copy client.
When you create a periodic snapshot task on a ZFS volume that is configured as a CIFS share in FreeNAS®, it is automatically configured to support shadow
copies.
Before using shadow copies with FreeNAS®, be aware of the following caveats:
- If the Windows system is not fully patched to the latest service pack, Shadow Copies may not work. If you are unable to see any previous versions of files
to restore, use Windows Update to make sure that the system is fully up-to-date.
- Shadow copy support only works for ZFS pools or datasets. This means that the CIFS share must be configured on a volume or dataset, not on a directory.
- Since directories can not be shadow copied at this time, if you configure “Enable home directories” on the CIFS service, any data stored in the
user’s home directory will not be shadow copied.
- Datasets are filesystems and shadow copies cannot traverse filesystems. If you want to be able to see the shadow copies in your child datasets, create
separate shares for them.
- shadow copies will not work with a manual snapshot, you must create a periodic snapshot task for the pool or dataset being shared by CIFS or a recursive
task for a parent dataset. At this time, if multiple snapshot tasks are created for the same pool/dataset being shared by CIFS, shadow copies will only
work on the last executed task at the time the CIFS service started. A future version of FreeNAS® will address this limitation.
- The periodic snapshot task should be created and at least one snapshot should exist before creating the CIFS share. If you created the CIFS share
first, restart the CIFS service in .
- Appropriate permissions must be configured on the volume/dataset being shared by CIFS.
- Users can not delete shadow copies on the Windows system due to the way Samba works. Instead, the administrator can remove snapshots from the FreeNAS®
administrative GUI. The only way to disable shadow copies completely is to remove the periodic snapshot task and delete all snapshots associated with the
CIFS share.
In this configuration example, a Windows 7 computer has two users: user1 and
user2. To configure FreeNAS® to provide shadow copy support:
- For the ZFS volume named /mnt/data, create two ZFS datasets in . The
first dataset is named /mnt/data/user1 and the second dataset is named /mnt/data/user2.
- If you are not using Active Directory or LDAP, create two users, user1 and
user2 in . Each user has the following attributes:
- “Username” and “Password” match that user’s username and password on the Windows system
- for the “Home Directory”, browse to the dataset created for that user
- Set the permissions on /mnt/data/user1 so that the Owner(user) and Owner(group) is user1. Set the permissions on /mnt/data/user2 so that
the “Owner(user)” and “Owner(group)” is user2. For each dataset’s permissions, tighten the “Mode” so that “Other” can not read or execute the
information on the dataset.
- Create two periodic snapshot tasks in , one for each dataset. Alternatively,
you can create one periodic snapshot task for the entire data volume.
Before continuing to the next step, confirm that at least one snapshot for each dataset is displayed in the “ZFS Snapshots” tab. When creating your
snapshots, keep in mind how often your users need to access modified files and during which days and time of day they are likely to make changes.
- Create two CIFS shares in . The first CIFS share is named user1 and has a
Path of /mnt/data/user1; the second CIFS share is named user2 and has a “Path” of /mnt/data/user2. When creating the first share, click
the “No” button when the pop-up button asks if the CIFS service should be started. When the last share is created, click the “Yes” button when the pop-up
button prompts to start the CIFS service. Verify that the CIFS service is set to “ON” in .
- From a Windows system, login as user1 and open . Two shares should appear, named
user1 and
user2. Due to the permissions on the datasets,
user1 should receive an error if they click on the
user2 share. Due to the permissions on the datasets,
user1 should be able to create, add, and delete files and folders from the
user1 share.
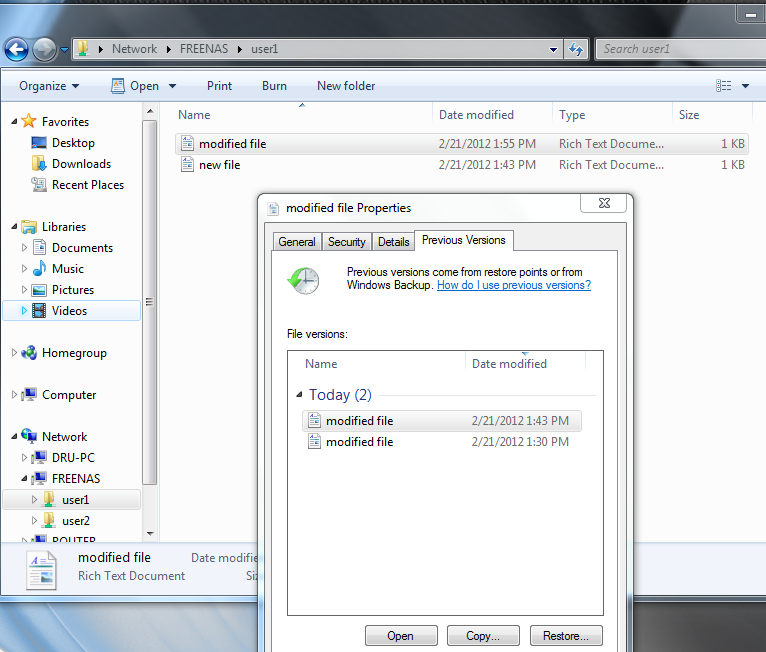
Figure 10.4e provides an example of using shadow copies while logged in as user1. In this example, the user right-clicked
modified file and selected “Restore previous versions” from the menu. This particular file has three versions: the current version, plus two previous
versions stored on the FreeNAS® system. The user can choose to open one of the previous versions, copy a previous version to the current folder, or restore
one of the previous versions, which will overwrite the existing file on the Windows system.
Figure 10.4e: Viewing Previous Versions within Explorer
10.5. Block (iSCSI)
iSCSI is a protocol standard for the consolidation of storage data. iSCSI allows FreeNAS® to act like a storage area network (SAN) over an existing Ethernet
network. Specifically, it exports disk devices over an Ethernet network that iSCSI clients (called initiators) can attach to and mount. Traditional SANs
operate over fibre channel networks which require a fibre channel infrastructure such as fibre channel HBAs, fibre channel switches, and discrete cabling.
iSCSI can be used over an existing Ethernet network, although dedicated networks can be built for iSCSI traffic in an effort to boost performance. iSCSI also
provides an advantage in an environment that uses Windows shell programs; these programs tend to filter “Network Location” but iSCSI mounts are not
filtered.
Before configuring the iSCSI service, you should be familiar with the following iSCSI terminology:
CHAP: an authentication method which uses a shared secret and three-way authentication to determine if a system is authorized to access the storage device
and to periodically confirm that the session has not been hijacked by another system. In iSCSI, the initiator (client) performs the CHAP authentication.
Mutual CHAP: a superset of CHAP in that both ends of the communication authenticate to each other.
Initiator: a client which has authorized access to the storage data on the FreeNAS® system. The client requires initiator software in order to initiate
the connection to the iSCSI share.
Target: a storage resource on the FreeNAS® system. Every target has a unique name known as an iSCSI Qualified Name (IQN).
Internet Storage Name Service (iSNS): protocol for the automated discovery of iSCSI devices on a TCP/IP network.
Extent: the storage unit to be shared. It can either be a file or a device.
Portal: indicates which IP(s) and port(s) to listen on for connection requests.
LUN: stands for Logical Unit Number and represents a logical SCSI device. An initiator negotiates with a target to establish connectivity to a LUN; the
result is an iSCSI connection that emulates a connection to a SCSI hard disk. Initiators treat iSCSI LUNs the same way as they would a raw SCSI or IDE hard
drive; rather than mounting remote directories, initiators format and directly manage filesystems on iSCSI LUNs. When configuring multiple iSCSI LUNs, create
a new target for each LUN. Since iSCSI multiplexes a target with multiple LUNs over the same TCP connection, you will experience contention from TCP if there
is more than one target per LUN.
In FreeNAS® 9.3, iSCSI is built into the kernel. This version of iSCSI supports Microsoft Offloaded Data Transfer (ODX), meaning that file copies happen
locally, rather than over the network. It also supports the following VAAI (vStorage APIs for Array Integration) primitives, where VAAI is VMware’s API
framework that enables certain storage tasks, such as large data moves, to be offloaded from the virtualization hardware to the storage array.
- unmap: tells ZFS that the space occupied by deleted files should be freed. Without unmap, ZFS is unaware of freed space made when the initiator deletes
files. For this feature to work, the initiator must support the unmap command.
- atomic test and set: allows multiple initiators to synchronize LUN access in a fine-grained manner rather than locking the whole LUN, which would
prevent other hosts from accessing the same LUN simultaneously.
- write same: when allocating virtual machines with thick provisioning, the necessary write of zeroes is done locally, rather than over the network, so
virtual machine creation is much quicker.
- xcopy: similar to Microsoft ODX, copies happen locally rather than over the network.
- stun: if a volume runs out of space, this feature pauses any running virtual machines so that the space issue can be fixed, instead of reporting write
errors.
- threshold warning: the system reports a warning when a configurable capacity is reached. In FreeNAS, this threshold can be configured both at the pool
level (see Table 10.5a) and the device extent level (see Table 10.5f).
- LUN reporting: the LUN reports that it is thin provisioned.
To take advantage of these VAAI primitives, create a zvol using the instructions in Create zvol and use it to create a device extent, as described in
Extents.
In order to configure iSCSI:
- Review the target global configuration parameters.
- Create at least one portal.
- Determine which hosts are allowed to connect using iSCSI and create an initiator.
- Decide if you will use authentication, and if so, whether it will be CHAP or mutual CHAP. If using authentication, create an authorized access.
- Create a target.
- Create either a device or a file extent to be used as storage.
- Associate a target with an extent.
- Start the iSCSI service in .
The rest of this section describes these steps in more detail.
10.5.1. Target Global Configuration
, shown in Figures 10.5a, contains settings that apply to all iSCSI shares. Table
10.5a summarizes the settings that can be configured in the Target Global Configuration screen.
Figure 10.5a: iSCSI Target Global Configuration Variables
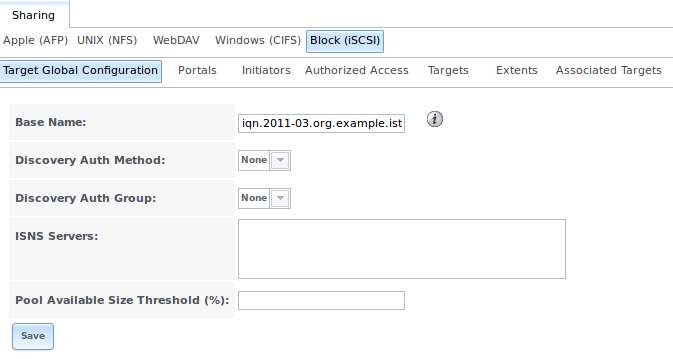
Table 10.5a: Target Global Configuration Settings
| Setting |
Value |
Description |
|---|
| Base Name |
string |
see the “Constructing iSCSI names using the iqn. format” section of RFC 3721
if you are unfamiliar with this format |
| Discovery Auth Method |
drop-down menu |
configures the authentication level required by the target for discovery of valid
devices, where None will allow anonymous discovery,
CHAP and
Mutual CHAP require authentication, and
Auto lets the initiator decide the authentication scheme |
| Discovery Auth Group |
drop-down menu |
depends on “Discovery Auth Method” setting: required if set to CHAP or
Mutual CHAP, optional if set to
Auto, and not needed if set to
None |
| ISNS Servers |
string |
space delimited list of hostnames or IP addresses of ISNS server(s) to register the
system’s iSCSI targets and portals with |
| Pool Available Space Threshold |
integer |
input the pool percentage; when the pool’s specified capacity is reached, the system will
issue an alert |
10.5.2. Portals
A portal specifies the IP address and port number to be used for iSCSI connections. will
bring up the screen shown in Figure 10.5b.
Table 10.5b summarizes the settings that can be configured when adding a portal. If you need to assign additional IP addresses to the portal, click the link
“Add extra Portal IP”.
Figure 10.5b: Adding an iSCSI Portal
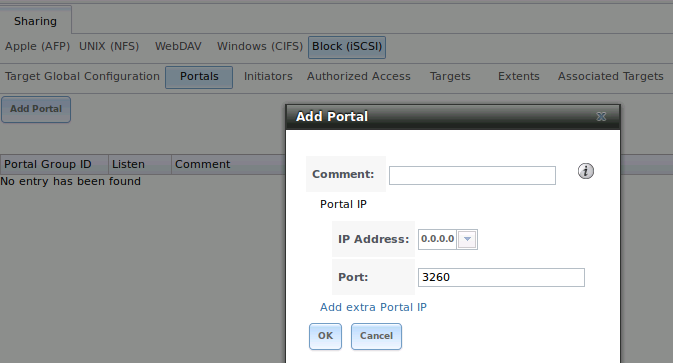
Table 10.5b: Portal Configuration Settings
| Setting |
Value |
Description |
|---|
| Comment |
string |
optional description; portals are automatically assigned a numeric group ID |
| IP address |
drop-down menu |
select the IP address associated with an interface or the wildcard address
of 0.0.0.0 (any interface) |
| Port |
integer |
TCP port used to access the iSCSI target; default is 3260 |
FreeNAS® systems with multiple IP addresses or interfaces can use a portal to provide services on different interfaces or subnets. This can be used to
configure multi-path I/O (MPIO). MPIO is more efficient than a link aggregation.
If the FreeNAS® system has multiple configured interfaces, portals can also be used to provide network access control. For example, consider a system with
four interfaces configured with the following addresses:
192.168.1.1/24
192.168.2.1/24
192.168.3.1/24
192.168.4.1/24
You could create a portal containing the first two IP addresses (group ID 1) and a portal containing the remaining two IP addresses (group ID 2). You could
then create a target named A with a Portal Group ID of 1 and a second target named B with a Portal Group ID of 2. In this scenario, istgt would listen on all
four interfaces, but connections to target A would be limited to the first two networks and connections to target B would be limited to the last two networks.
Another scenario would be to create a portal which includes every IP address except for the one used by a management interface. This would prevent iSCSI
connections to the management interface.
10.5.3. Initiators
The next step is to configure authorized initiators, or the systems which are allowed to connect to the iSCSI targets on the FreeNAS® system. To configure
which systems can connect, use , shown in Figure 10.5c.
Figure 10.5c: Adding an iSCSI Initiator
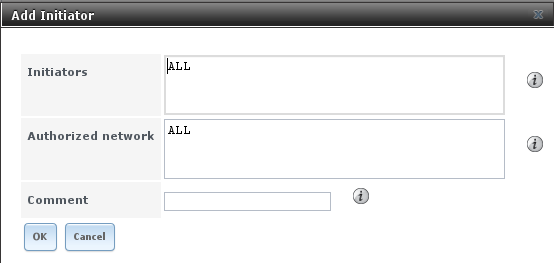
Table 10.5c summarizes the settings that can be configured when adding an initiator.
Table 10.5c: Initiator Configuration Settings
| Setting |
Value |
Description |
|---|
| Initiators |
string |
use ALL keyword or a list of initiator hostnames separated by commas or spaces |
| Authorized network |
string |
use ALL keyword or a network address with CIDR mask such as
192.168.2.0/24 |
| Comment |
string |
optional description |
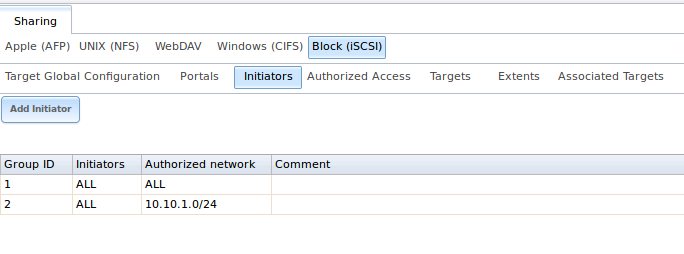
In the example shown in Figure 10.5d, two groups have been created. Group 1 allows connections from any initiator on any network; Group 2 allows connections
from any initiator on the 10.10.1.0/24 network. Click an initiator’s entry to display its “Edit” and “Delete” buttons.
Note
if you delete an initiator, a warning will indicate if any targets or target/extent mappings depend upon the initiator. If you confirm the delete,
these will be deleted as well.
Figure 10.5d: Sample iSCSI Initiator Configuration
10.5.4. Authorized Accesses
If you will be using CHAP or mutual CHAP to provide authentication, you must create an authorized access in
. This screen is shown in Figure 10.5e.
Note
this screen sets login authentication. This is different from discovery authentication which is set in Target Global Configuration.
Figure 10.5e: Adding an iSCSI Authorized Access
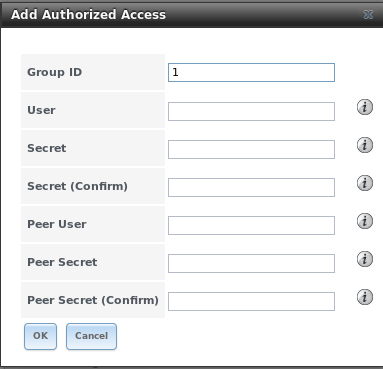
Table 10.5d summarizes the settings that can be configured when adding an authorized access:
Table 10.5d: Authorized Access Configuration Settings
| Setting |
Value |
Description |
|---|
| Group ID |
integer |
allows different groups to be configured with different authentication profiles; for instance, all users with a Group ID of 1
will inherit the authentication profile associated with Group 1 |
| User |
string |
name of user account to create for CHAP authentication with the user on the remote system; many initiators default to using the
initiator name as the user |
| Secret |
string |
password to be associated with “User”; the iSCSI standard requires that this be at least 12 characters long |
| Peer User |
string |
only input when configuring mutual CHAP; in most cases it will need to be the same value as “User” |
| Peer Secret |
string |
the mutual secret password which must be different than the “Secret”; required if the
“Peer User” is set |
Note
CHAP does not work with GlobalSAN initiators on Mac OS X.
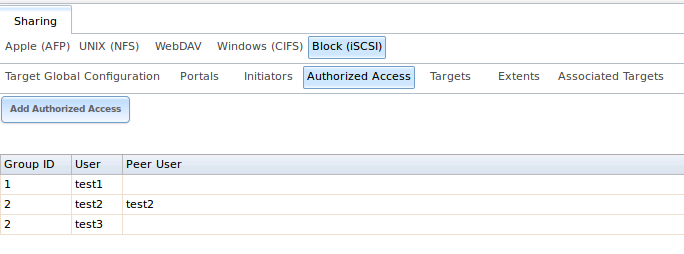
As authorized accesses are added, they will be listed under View Authorized Accesses. In the example shown in Figure 10.5f, three users (test1,
test2, and
test3) and two groups (
1 and
2) have been created, with group 1 consisting of one CHAP user and group 2 consisting of one mutual CHAP user and one CHAP user. Click an authorized access
entry to display its “Edit” and “Delete” buttons.
Figure 10.5f: Viewing Authorized Accesses
10.5.5. Targets
Next, create a Target using , as shown in Figure 10.5g. A target combines a portal ID,
allowed initiator ID, and an authentication method. Table 10.5e summarizes the settings that can be configured when creating a Target.
Note
an iSCSI target creates a block device that may be accessible to multiple initiators. A clustered filesystem is required on the block device, such
as VMFS used by VMware ESX/ESXi, in order for multiple initiators to mount the block device read/write. If a traditional filesystem such as EXT, XFS, FAT,
NTFS, UFS, or ZFS is placed on the block device, care must be taken that only one initiator at a time has read/write access or the result will be
filesystem corruption. If you need to support multiple clients to the same data on a non-clustered filesystem, use CIFS or NFS instead of iSCSI or create
multiple iSCSI targets (one per client).
Figure 10.5g: Adding an iSCSI Target
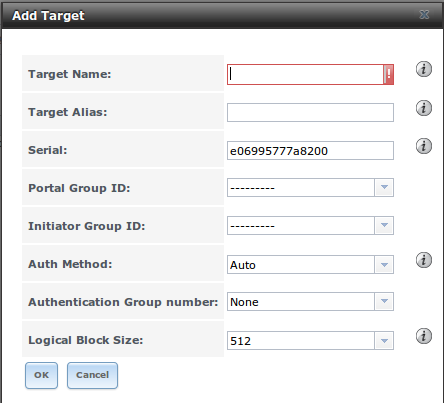
Table 10.5e: Target Settings
| Setting |
Value |
Description |
|---|
| Target Name |
string |
required value; base name will be appended automatically if it does not start with iqn |
| Target Alias |
string |
optional user-friendly name |
| Serial |
string |
unique ID for target to allow for multiple LUNs; the default is generated from the system’s MAC address |
| Portal Group ID |
drop-down menu |
leave empty or select number of existing portal to use |
| Initiator Group ID |
drop-down menu |
select which existing initiator group has access to the target |
| Auth Method |
drop-down menu |
choices are None,
Auto,
CHAP, or
Mutual CHAP |
| Authentication Group number |
drop-down menu |
None or integer representing number of existing authorized access |
| Logical Block Size |
drop-down menu |
should only be changed to emulate a physical disk’s size or to increase the block size to allow for larger
filesystems on an operating system limited by block count |
10.5.6. Extents
In iSCSI, the target virtualizes something and presents it as a device to the iSCSI client. That something can be a device extent or a file extent:
Device extent: virtualizes an unformatted physical disk, RAID controller, zvol, zvol snapshot, or an existing
HAST device.
Virtualizing a single disk is slow as there is no caching but virtualizing a hardware RAID controller has higher performance due to its cache. This type of
virtualization does a pass-through to the disk or hardware RAID controller. None of the benefits of ZFS are provided and performance is limited to the
capabilities of the disk or controller.
Virtualizing a zvol adds the benefits of ZFS such as its read cache and write cache. Even if the client formats the device extent with a different filesystem,
as far as FreeNAS® is concerned, the data benefits from ZFS features such as block checksums and snapshots. A zvol is also required in order to take
advantage of VAAI primitives and should be used when using virtualization software as the iSCSI initiator.
File extent: allows you to export a portion of a ZFS volume. The advantage of a file extent is that you can create multiple exports per volume.
Warning
for performance reasons and to avoid excessive fragmentation, it is recommended to keep the used space of an extent below 50%. As required, you
can increase the capacity of an extent using the instructions in Growing LUNs.
To add an extent, go to . In the example shown in Figure 10.5h, the device extent is using the
export zvol that was previously created from the /mnt/volume1 volume.
Note
in FreeNAS® versions prior to 8.3.1, if a physical disk was used instead of a zvol to create a device extent, a bug wiped the partition table on
the disk, resulting in data loss. This bug was fixed in 8.3.1.
Table 10.5f summarizes the settings that can be configured when creating an extent. Note that
file extent creation will fail if you do not append the name of the file to be created to the volume/dataset name.
Figure 10.5h: Adding an iSCSI Extent
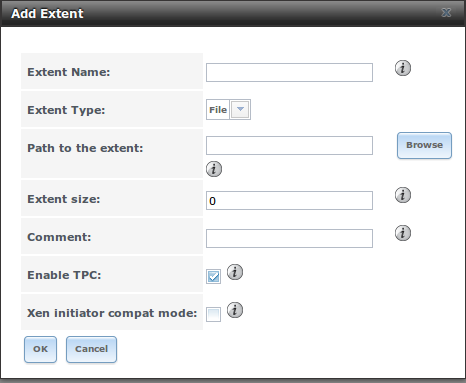
Table 10.5f: Extent Configuration Settings
| Setting |
Value |
Description |
|---|
| Extent Name |
string |
name of extent; if the “Extent size” is not 0, it can not be an existing file within the volume/dataset |
| Extent Type |
drop-down menu |
select from File or
Device |
| Path to the extent |
browse button |
only appears if File is selected; either browse to an existing file and use
0 as the “Extent size”,
or browse to the volume or dataset, click the “Close” button, append the “Extent Name” to the path, and specify
a value in “Extent size” |
| Device |
drop-down menu |
only appears if Device is selected; select the unformatted disk, controller, zvol, zvol snapshot, or HAST device |
| Extent size |
integer |
only appears if File is selected; if the size is specified as
0, the file must already exist and the actual file size will be used; otherwise specifies the size of the file to
create |
| Available Size
Threshold |
string |
only appears if a zvol is selected as the “Device”; when the specified capacity is reached, the system will issue an
alert |
| Comment |
string |
optional |
| Enable TPC |
checkbox |
if checked, an initiator can bypass normal access control and access any scannable target; this allows
xcopy operations otherwise blocked by access control |
| Xen initiator
compat mode |
checkbox |
check this box when using Xen as the iSCSI initiator |
10.5.7. Target/Extents
The last step is associating an extent to a target within . This screen is
shown in Figure 10.5i. Use the drop-down menus to select the existing target and extent.
Table 10.5g summarizes the settings that can be configured when associating targets and extents.
Table 10.5g: Target/Extents Configuration Settings
| Setting |
Value |
Description |
|---|
| LUN ID |
drop-down menu |
specify the ID of the LUN; the default of Auto will select the next available LUN ID, starting at 0 |
| Target |
drop-down menu |
select the pre-created target |
| Extent |
drop-down menu |
select the pre-created extent |
It is recommended to always associate extents to targets in a 1:1 manner, even though the GUI will allow multiple extents to be associated with the same
target.
Once iSCSI has been configured, don’t forget to start it in . Click the red “OFF” button next to iSCSI. After a
second or so, it will change to a blue ON, indicating that the service has started.
10.5.8. Connecting to iSCSI
In order to access the iSCSI target, clients will need to use iSCSI initiator software.
An iSCSI Initiator client is pre-installed with Windows 7. A detailed how-to for this client can be found
here. A client for Windows 2000, XP, and 2003 can be found
here. This
how-to
shows how to create an iSCSI target for a Windows 7 system.
Mac OS X does not include an initiator.
globalSAN
is a commercial, easy-to-use Mac initiator.
BSD systems provide command line initiators:
iscontrol(8)
comes with FreeBSD versions 9.x and lower,
iscsictl(8)
comes with FreeBSD versions 10.0 and higher,
iscsi-initiator(8)
comes with NetBSD, and
iscsid(8)
comes with OpenBSD.
Some Linux distros provide the command line utility iscsiadm from
Open-iSCSI. Use a web search to see if a package exists for your distribution should the command not exist on your Linux
system.
If you add a LUN while iscsiadm is already connected, it will not see the new LUN until you rescan using iscsiadm -m node -R.
Alternately, use iscsiadm -m discovery -t st -p portal_IP to find the new LUN and iscsiadm -m node -T LUN_Name -l to log into the LUN.
Instructions for connecting from a VMware ESXi Server can be found at
How to configure FreeNAS 8 for iSCSI and connect to ESX(i). Note that the
requirements for booting vSphere 4.x off iSCSI differ between ESX and ESXi. ESX requires a hardware iSCSI adapter while ESXi requires specific iSCSI boot
firmware support. The magic is on the booting host side, meaning that there is no difference to the FreeNAS® configuration. See the
iSCSI SAN Configuration Guide
for details.
If you can see the target but not connect to it, check the “Discovery Auth” settings in “Target Global Configuration”.
If the LUN is not discovered by ESXi, make sure that promiscuous mode is set to “Accept” in the vSwitch.
10.5.9. Growing LUNs
The method used to grow the size of an existing iSCSI LUN depends on whether the LUN is backed by a file extent or a zvol. Both methods are described in this
section.
After the LUN is expanded using one of the methods below, use the tools from the initiator software to grow the partitions and the filesystems it contains.
10.5.9.1. Zvol Based LUN
To grow a zvol based LUN, go to , highlight the zvol to be grown, and click its “Edit zvol” button. In
the example shown in Figure 10.5j, the current size of the zvol named zvol1 is 4GB.
Figure 10.5j: Editing an Existing Zvol
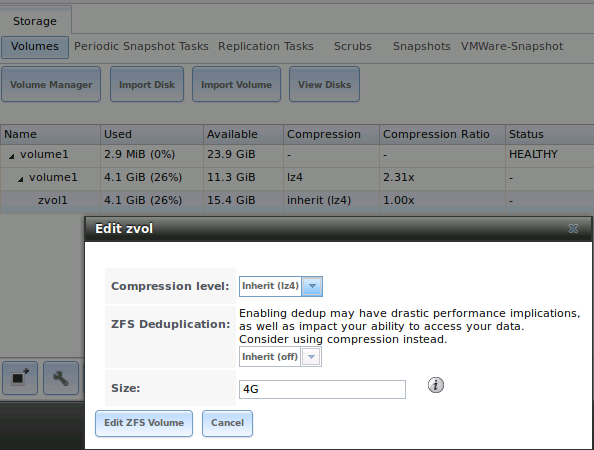
Input the new size for the zvol in the “Size” field and click the “Edit ZFS Volume” button. This menu will close and the new size for the zvol will
immediately show in the “Used” column of the “View Volumes” screen.
10.5.9.2. File Extent Based LUN
To grow a file extent based LUN, go to to determine the path of the file extent to
grow. Open Shell to grow the extent. This example grows /mnt/volume1/data by 2G:
truncate -s +2g /mnt/volume1/data
Go back to and click the “Edit” button for the file extent. Set the size to 0 as
this causes the iSCSI target to use the new size of the file.























